The cannabis concentrate industry represents one of the most complex and rapidly evolving sectors within the legal cannabis market, where product innovation, regulatory compliance, and consumer safety intersect in unprecedented ways. Part I of this comprehensive guide explores the foundational elements that define the concentrate landscape: the diverse array of products available to consumers, the intricate regulatory frameworks governing their production and distribution, and the sophisticated packaging solutions required to meet both compliance standards and market demands. Understanding these interconnected components is essential for industry professionals, investors, and consumers alike, as they form the backbone of a market projected to reach billions in value over the next decade.
From the glass-like clarity of shatter to the complex terpene profiles of live rosin, cannabis concentrates encompass a vast spectrum of products, each with distinct production methods, potency levels, and consumer applications. However, this product diversity exists within a labyrinthine regulatory environment where federal prohibition meets state-level legalization, creating unique compliance challenges that vary dramatically across jurisdictions. The packaging that ultimately delivers these products to consumers must navigate child-resistant requirements, tamper-evident standards, and comprehensive labeling mandates while simultaneously serving as a critical brand differentiator in an increasingly competitive marketplace. This section provides the essential knowledge needed to understand how product science, regulatory compliance, and packaging innovation work together to shape the modern cannabis concentrate industry.

Extraction Methods and Categories
Cannabis concentrates are produced through various extraction techniques, each offering distinct advantages in terms of yield, purity, and flavor preservation. The industry has evolved from rudimentary extraction methods to sophisticated technological processes that maximize cannabinoid recovery while maintaining product safety and consistency.
Solvent-Based Extractions dominate commercial production due to their efficiency and scalability. Trulieve Cannabis Corp., a leading multi-state operator, utilizes various extraction techniques including supercritical ethanol extraction, carbon dioxide extraction, hydrocarbon extraction, and mechanical separation. The company has particularly invested in light hydrocarbon extraction, which typically offers higher yields than other extraction methods and allows for concentrates that preserve the natural ratios of cannabinoids, terpenes, and other target compounds to better replicate the flower experience.
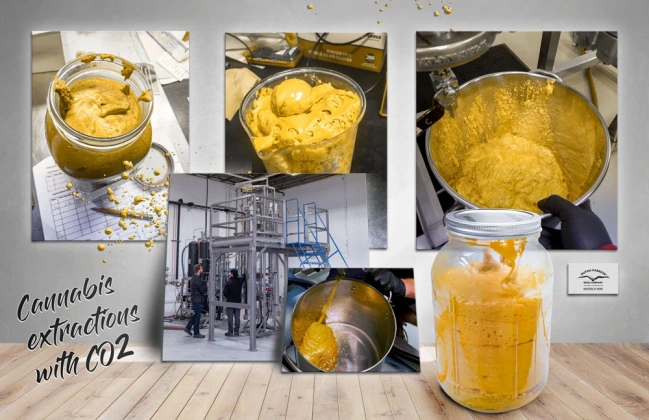
CO2 extraction has emerged as the industry gold standard, praised for its ability to produce high-purity extracts without harmful residual solvents. This method preserves the full spectrum of cannabinoids, terpenes, and other beneficial compounds found in the cannabis plant, resulting in a more potent and therapeutic product. The technique is environmentally friendly and produces consistent, safe products that meet stringent regulatory requirements.
Ethanol extraction and carbon dioxide extraction techniques offer different benefits than hydrocarbon extraction and are each used for specific purposes, such as production of oil for use in manufactured goods and targeted extraction of specific compounds. These methods allow producers to create specialized products tailored to specific medical applications or consumer preferences.
Solventless Extractions have gained significant traction among consumers seeking additive-free products. Methods such as rosin pressing use heat and pressure to extract cannabinoids without chemical solvents, appealing to health-conscious consumers and artisanal producers. Ice water extraction and dry sift techniques also fall into this category, producing what many consider “cleaner” concentrates.

Popular Concentrate Types
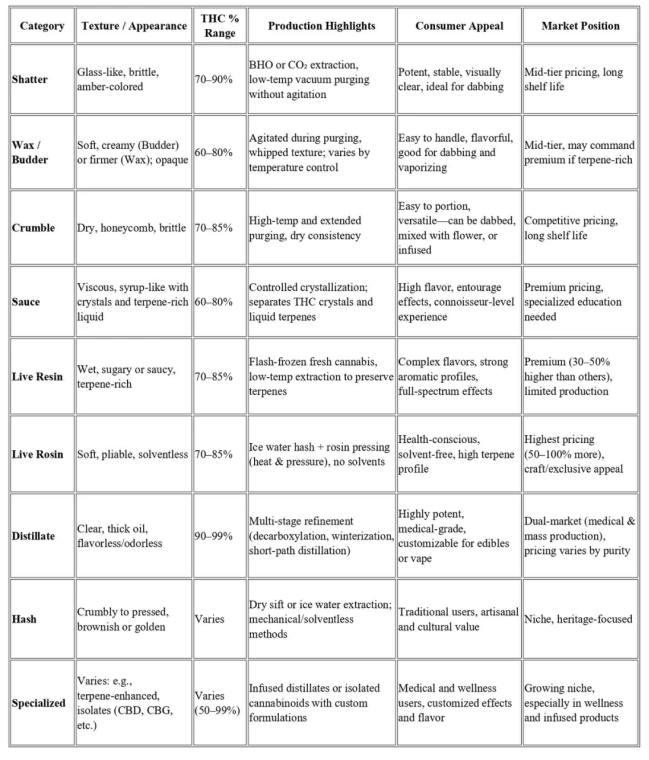
The concentrate market encompasses a diverse array of products, each distinguished by texture, potency, and production method. Understanding these categories is essential for businesses operating in this space, as consumer preferences, production costs, and market positioning vary significantly across different concentrate types.
Texture-Based Categories
Texture-based classification represents the most common system used by consumers and retailers, with each category offering distinct advantages for different consumption methods and user preferences.
Shatter
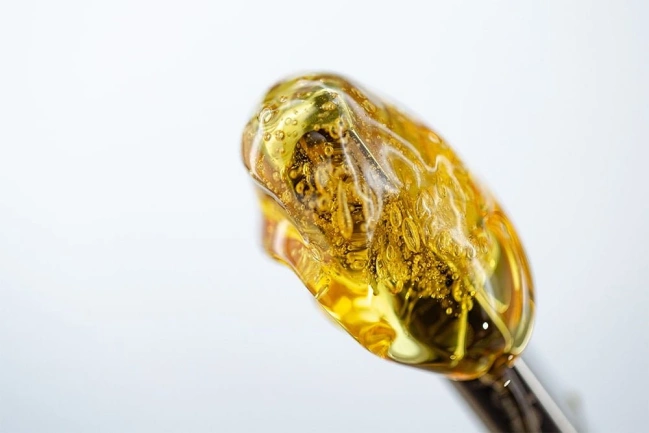
Shatter represents one of the most recognizable concentrate forms, characterized by its glass-like, brittle consistency that resembles amber-colored glass. This concentrate typically contains 70-90% THC, making it among the most potent cannabis products available to consumers.
Production Process: Shatter is created through butane hash oil (BHO) or CO2 extraction followed by careful purging processes that remove residual solvents. The key to achieving shatter’s distinctive texture lies in maintaining low temperatures during the purging process and avoiding agitation that could introduce air bubbles or alter the molecular structure. The final product undergoes vacuum purging at temperatures typically ranging from 80-100°F to ensure complete solvent removal while preserving the glassy consistency.
Consumer Preferences: Shatter appeals to experienced cannabis users who prioritize potency and visual appeal. Its stable consistency makes it ideal for dabbing, as it doesn’t stick to tools and provides consistent dosing. The transparent appearance allows consumers to assess quality and purity visually, making it a preferred choice for those who value product clarity.
Market Position: Shatter typically commands mid-tier pricing in the concentrate market, positioned between basic wax products and premium live resins. Its long shelf life and stable consistency make it attractive to both consumers and retailers, as it maintains quality over extended periods when stored properly.

Wax/Budder
Wax and Budder represent closely related concentrate forms with soft, malleable textures ranging from creamy to whipped consistency. These concentrates typically contain 60-80% THC and are often preferred for their ease of handling and consistent dosing capabilities.
Production Process: Wax and budder are created through similar extraction methods as shatter but undergo different post-processing techniques. The key difference lies in the purging process, where the concentrate is agitated or whipped during purging, introducing air and creating the characteristic opaque, creamy texture. Temperature control during this process determines whether the final product becomes wax (firmer consistency) or budder (creamier texture).
Texture Variations:
– Budder: Smooth, creamy consistency similar to cake frosting, easily scooped with tools
– Wax: Slightly firmer than budder, with a consistency similar to lip balm or soft cheese
– Crème: The softest variation, almost liquid at room temperature
Consumer Appeal: These concentrates attract users who value ease of use and consistent dosing. The malleable texture makes them ideal for vaporizing and dabbing, while the opaque appearance often indicates higher terpene content compared to shatter, resulting in enhanced flavor profiles.
Market Considerations: Wax and budder typically retail at similar price points to shatter but may command premium pricing when produced with high-terpene strains or specialized extraction techniques. Their shorter shelf life compared to shatter requires proper storage and faster inventory turnover.

Crumble
Crumble features a dry, honeycomb-like texture that breaks apart easily, offering convenience for various consumption methods. This concentrate typically contains 70-85% THC and appeals to users who prefer easy handling and versatile application.
Production Process: Crumble is created through purging at higher temperatures than shatter, typically 100-110°F, combined with extended purging times. This process removes moisture and residual solvents while creating the characteristic dry, crumbly texture. Some producers achieve crumble consistency by pre-purging other concentrates and then re-processing them at higher temperatures.
Texture Characteristics:
– Dry, brittle consistency that breaks apart easily
– Honeycomb or sugar-like appearance
– Easy to portion without specialized tools
– Minimal stickiness compared to other concentrates
Consumer Benefits: Crumble’s dry texture makes it ideal for sprinkling on flower or mixing into edibles. The easy portioning appeals to users who want consistent dosing without specialized tools. Its versatility makes it suitable for multiple consumption methods, from dabbing to vaporizing to infusion.
Market Position: Crumble typically commands competitive pricing due to its production efficiency and broad consumer appeal. Its extended shelf life and stable consistency make it attractive to retailers managing inventory across multiple product categories.

Sauce
Sauce represents a viscous concentrate containing both liquid terpenes and crystalline structures, prized for their complex flavor profiles and high terpene content. This concentrate typically contains 60-80% THC but distinguishes itself through exceptional terpene preservation.
Production Process: Sauce requires specialized extraction and separation techniques that preserve terpene integrity while allowing THC crystallization. The process typically involves initial extraction followed by controlled crystallization in temperature-controlled environments. Terpenes separate from cannabinoids during this process, creating the characteristic sauce-like consistency with visible crystals.
Texture Components:
– Liquid terpene fraction: Provides flavor and aroma
– Crystalline structures: Concentrated THC formations
– Viscous consistency: Resembles honey or syrup
– Heterogeneous appearance: Visible separation of components
Consumer Appeal: Sauce attracts connoisseur consumers who prioritize flavor complexity and terpene effects. The high terpene content provides enhanced entourage effects and distinctive flavor profiles that appeal to users seeking premium experiences.
Market Position: Sauce typically commands premium pricing due to complex production requirements and specialized equipment needs. Its appeal to connoisseur consumers allows for higher profit margins but requires educational marketing to communicate value proposition.

Premium Categories
Premium concentrate categories command higher prices and represent the fastest-growing market segments, driven by consumer demand for enhanced quality, specialized production methods, and superior user experiences.
Live Resin
Live Resin represents the pinnacle of terpene preservation, produced from fresh-frozen cannabis plants that maintain maximum terpene content and deliver enhanced flavor profiles. This concentrate typically contains 70-85% THC with exceptional terpene concentrations ranging from 5-15%.
Production Process: Live resin production begins with flash-freezing freshly harvested cannabis at temperatures below -10°F immediately after harvest. This process preserves volatile terpenes that would otherwise degrade during traditional drying and curing. Specialized extraction equipment capable of processing frozen material is required, along with temperature-controlled environments throughout the extraction process.
Quality Factors:
– Harvest timing: Plants must be frozen within hours of harvest
– Storage conditions: Consistent sub-zero temperatures until processing
– Extraction parameters: Lower temperatures and reduced processing times
– Terpene preservation: Specialized techniques to maintain volatile compounds
Consumer Experience: Live resin provides superior flavor profiles that closely resemble fresh cannabis flowers. The high terpene content delivers enhanced entourage effects and complex aromatic experiences that distinguish it from other concentrate types.
Market Position: Live resin commands premium pricing, typically 30-50% higher than standard concentrates. Its appeal to connoisseur consumers and limited production capacity support higher profit margins but require specialized marketing and consumer education.

Live Rosin
Live Rosin represents the ultimate solventless concentrate, combining live processing benefits with chemical-free extraction methods. This concentrate typically contains 70-85% THC with exceptional terpene preservation and no residual solvents.
Production Process: Live rosin production combines fresh-frozen cannabis with solventless extraction techniques using heat and pressure. The process typically involves ice water extraction to create fresh-frozen bubble hash, followed by rosin pressing using specialized hydraulic presses at controlled temperatures typically ranging from 160-220°F.
Quality Considerations:
– Starting material quality: Premium fresh-frozen cannabis
– Extraction efficiency: Optimal pressure and temperature parameters
– Filtration methods: Multiple micron screens for purity
– Processing timing: Minimal exposure to heat and air
Consumer Appeal: Live rosin attracts health-conscious consumers seeking solventless products with maximum terpene preservation. The chemical-free production appeals to users concerned about residual solvents and processing additives.
Market Position: Live rosin commands highest premium pricing in the concentrate market, often 50-100% higher than standard concentrates. Limited production capacity and specialized equipment requirements support exclusive market positioning.

Distillates
Distillates represent highly refined concentrates containing 90%+ THC, offering maximum potency for medical applications requiring precise dosing. These concentrates undergo multiple purification processes to achieve pharmaceutical-grade purity.
Production Process: Distillate production involves multi-stage refinement including decarboxylation, winterization, and molecular distillation. The process removes plant materials, residual solvents, and impurities while concentrating specific cannabinoids. Short-path distillation equipment operating under vacuum conditions enables precise separation of different compounds.
Purity Characteristics:
– Cannabinoid concentration: 90-99% pure THC or CBD
– Terpene removal: Odorless and flavorless
– Contaminant elimination: Pesticides, heavy metals, and solvents removed
– Consistent potency: Batch-to-batch uniformity
Medical Applications: Distillates provide precise dosing for medical patients requiring consistent cannabinoid delivery. The high purity enables accurate dosing calculations and predictable effects, making them ideal for pharmaceutical applications.
Consumer Versatility: Distillates offer maximum versatility for product infusion, including edibles, vape cartridges, and topical applications. The neutral flavor profile allows for custom terpene addition and product formulation flexibility.
Market Position: Distillates serve dual markets, providing premium options for medical patients and cost-effective base materials for manufactured products. Pricing varies significantly based on purity levels and intended applications.

Additional Concentrate Categories
Hash and Traditional Concentrates
Traditional hash maintains cultural significance and artisanal appeal in the concentrate market. Dry sift hash and ice water hash represent solventless methods that appeal to traditionalist consumers and craft producers.
Production Methods:
– Dry sift: Mechanical separation using screens and agitation
– Ice water extraction: Trichome separation using ice water and filtration
– Traditional pressing: Heat and pressure application for consistency changes
Specialized Formulations
Terpene-enhanced concentrates represent emerging market segments where natural or botanical terpenes are reintroduced to distillates or other refined concentrates. These products offer customized flavor profiles and enhanced effects while maintaining high potency.
Cannabinoid-specific concentrates including CBD isolates, CBG concentrates, and minor cannabinoid formulations serve specialized medical applications and wellness markets.

Cannabis Concentrate Packaging Compliance
Cannabis concentrate packaging must navigate a complex web of federal, state, and local regulations designed to ensure product safety, prevent diversion, and protect public health. The regulatory framework varies significantly across jurisdictions, creating substantial challenges for multi-state operators and manufacturers who must maintain compliance across multiple legal frameworks while ensuring operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Federal Oversight and Constraints
Despite state-level legalization, cannabis remains a Schedule I controlled substance under federal law, creating a unique regulatory environment where state-licensed businesses operate in conflict with federal prohibition. This creates several compliance challenges:
Banking and Financial Services: Federal banking regulations limit access to traditional financial services, affecting how businesses manage compliance costs and operational expenses related to packaging and labeling requirements.
Interstate Commerce Restrictions: Federal prohibition prevents interstate transport of cannabis products, requiring each state to maintain independent supply chains and separate packaging facilities, increasing compliance complexity and costs for multi-state operators.
Federal Agency Involvement: While the FDA does not regulate cannabis products, other federal agencies maintain oversight responsibilities. The Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) sets standards for child-resistant packaging that states often adopt, while the DEA maintains authority over controlled substance regulations that can impact state-licensed operations.
Potential Rescheduling: Industry discussions around rescheduling cannabis from Schedule I to Schedule III could significantly impact regulatory frameworks, potentially introducing FDA oversight and pharmaceutical-style packaging requirements that would affect concentrate packaging standards.
Federal Taxation: Section 280E of the Internal Revenue Code prevents cannabis businesses from deducting ordinary business expenses, including packaging costs, creating additional financial pressures on compliance investments.

State-Level Regulatory Frameworks
Universal Child-Resistant Packaging Requirements
Child-Resistant Packaging represents a universal requirement across legal cannabis markets, though specific implementation varies by jurisdiction. These requirements stem from public health concerns and regulatory priority to prevent accidental consumption by minors.
Washington State Requirements
Washington State maintains comprehensive packaging regulations through the Washington State Liquor and Cannabis Board (WSLCB). Dispensaries can only sell cannabis products that are appropriately packaged and labeled, following WSLCB rules. The state’s requirements include:
Mandatory Child-Resistant Features: All cannabis products must be stored in child-resistant, tamper-evident packaging that complies with 16 CFR 1700.20 standards established by the Consumer Product Safety Commission. This includes:
– Push-and-turn caps for rigid containers
– Squeeze-and-pull mechanisms for flexible packaging
– Multi-step access systems that require coordinated movements
Minor Protection Measures: Retailers are prohibited from displaying products in a way that is attractive to minors, requiring opaque packaging and restricted visibility of cannabis products in retail environments.
Tamper-Evident Requirements: All packaging must include tamper-evident seals that provide clear visual indication if products have been opened or compromised, ensuring product integrity throughout the distribution chain.
California Regulatory Framework
California maintains some of the most stringent cannabis packaging requirements in the United States, reflecting the state’s commitment to public safety and regulatory compliance.
Secure Storage Requirements: The state mandates that cannabis businesses store all cannabis and cannabis products in a secured, locked room or a vault, with specific requirements for:
– Physical security measures including locks, alarms, and surveillance systems
– Access controls limiting personnel who can handle packaged products
– Inventory tracking throughout storage and distribution

Packaging Specifications: California requires tamper-evident seals and opaque packaging to prevent unauthorized access and ensure product integrity throughout the supply chain. Specific requirements include:
– Opaque materials that prevent visual identification of contents
– Tamper-evident closures that show clear evidence of opening
– Child-resistant mechanisms meeting federal CPSC standards
– Resealable features for multi-use products
Advertising and Marketing Restrictions: California prohibits packaging that appeals to minors, including:
– Cartoon characters or youth-oriented imagery
– Bright colors or attractive designs that might appeal to children
– Candy-like appearances or food product similarities
Comprehensive Labeling Requirements
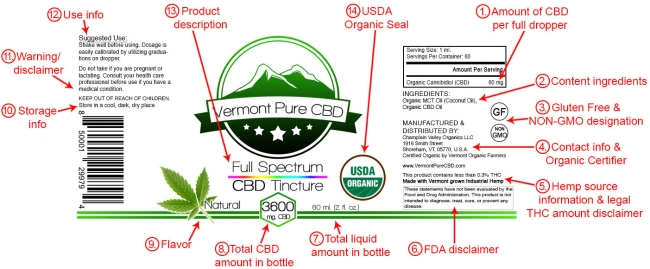
Labeling Requirements encompass comprehensive information disclosure across all legal markets, with specific mandates varying by jurisdiction but generally including similar core elements.
Mandatory Label Information
Product Potency Disclosure: All cannabis concentrate labels must include accurate THC/CBD content expressed in both milligrams per package and percentage by weight. This information must be:
– Clearly visible and easily readable
– Prominently displayed on the principal display panel
– Verified by third-party laboratory testing
– Batch-specific and traceable to testing results
Ingredient Lists: Complete ingredient disclosure including:
– Cannabis extract source and type
– Carrier oils or thinning agents
– Flavoring agents and additives
– Allergen warnings where applicable
Serving Size Information: For products intended for consumption, labels must specify:
– Recommended serving size in milligrams of THC
– Number of servings per package
– Onset time and duration expectations
Health and Safety Warnings: Standardized warning statements addressing:
– Psychoactive effects and impairment risks
– Pregnancy and breastfeeding warnings
– Operating machinery and driving restrictions
– Keep out of reach of children statements
Batch Tracking and Traceability
Batch Tracking Information allows products to be traced from cultivation through final sale, supporting regulatory compliance and public safety through comprehensive supply chain monitoring.
Seed-to-Sale Tracking Systems: Many states require comprehensive tracking using systems like Washington’s Marijuana Tracking System (MTS), which monitors:
– Cultivation activities including planting, harvesting, and processing
– Manufacturing processes including extraction, packaging, and labeling
– Distribution activities including wholesale and retail transactions
– Inventory management throughout the supply chain
Unique Identifier Requirements: Each product package must include:
– Unique batch numbers linking to specific cultivation and processing runs
– Manufacturing dates and expiration dates
– Laboratory testing identification numbers
– Traceability codes for supply chain monitoring
Multi-State Compliance Challenges
Multi-state operators face significant challenges managing regulatory variation across different jurisdictions, each with unique requirements and compliance standards.
Container Requirements: States maintain different specifications for acceptable packaging materials:
– Glass containers: Some states require specific thickness or break-resistance standards
– Plastic containers: Various states specify different acceptable polymer types
– Flexible packaging: Child-resistant requirements vary significantly across jurisdictions
Labeling Format Variations: Different states require different label formats:
– Label placement requirements vary by state
– Text size and font requirements differ across jurisdictions
– Color requirements for warnings and safety information
– Language requirements in multilingual markets
Laboratory Testing Requirements: States maintain different testing standards:
– Potency testing protocols vary in precision and methodology
– Contaminant testing includes different panels and detection limits
– Residual solvent testing requirements differ significantly
– Microbial testing standards vary across jurisdictions

Quality Assurance Protocols: Different states require different quality control measures:
– Batch release protocols vary in complexity
– Stability testing requirements differ across jurisdictions
– Recall procedures maintain different notification and response requirements
Standardized Procedures: Multi-state operators often implement centralized compliance management systems that:
– Exceed minimum requirements across all jurisdictions
– Standardize packaging specifications to the most restrictive standards
– Implement uniform quality control procedures
– Maintain consistent labeling across all markets
Technology Solutions: Advanced operators utilize compliance management software that:
– Tracks regulatory changes across multiple jurisdictions
– Manages labeling requirements for different markets
– Monitors testing requirements and batch tracking
– Ensures inventory compliance across multiple facilities
Regulatory Risk Assessment: Operators must evaluate compliance risks including:
– Regulatory changes and enforcement priorities
– Penalties and sanctions for non-compliance
– Market access restrictions from regulatory violations
– Reputation risks from compliance failures
Compliance Investment Strategies: Successful operators balance compliance costs with operational efficiency:
– Packaging standardization reduces complexity and costs
– Automated compliance systems improve accuracy and efficiency
– Regular compliance audits identify and address potential issues
– Legal counsel ensures ongoing regulatory compliance
Packaging Design
Container Materials
The selection of appropriate packaging materials for cannabis concentrates requires careful consideration of product preservation, regulatory compliance, and consumer safety. Different concentrate types demand specific packaging solutions to maintain quality and potency over time.
Glass containers remain the preferred choice for premium concentrates due to their inert properties and ability to preserve product quality. Glass does not interact with cannabinoids or terpenes, ensuring that concentrates maintain their intended potency and flavor profiles throughout their shelf life. However, glass packaging must incorporate child-resistant mechanisms and tamper-evident features to meet regulatory requirements.

Silicone containers gained popularity for their non-stick properties, making them convenient for consumers handling sticky concentrates. However, industry research has revealed potential issues with terpene degradation in certain silicone formulations, leading some premium producers to seek alternative materials.
PTFE (Teflon) and FEP (Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene) containers offer superior non-stick properties without the potential terpene interaction issues associated with some silicone products. These materials provide optimal preservation for high-terpene concentrates while maintaining regulatory compliance.
Child-resistant mechanisms vary by product type and container design. Common solutions include push-and-turn caps for glass jars, squeeze-and-pull systems for flexible containers, and multi-step access mechanisms for specialized packaging. The challenge lies in balancing accessibility for adult consumers with child safety requirements.
Visual Identity and Brand Differentiation
Packaging design serves as the primary consumer touchpoint, requiring sophisticated approaches that balance regulatory compliance with brand differentiation and consumer appeal. Effective design communicates product quality, brand values, and usage instructions while meeting strict regulatory requirements.
Color Psychology and Brand Positioning:
– Premium black and gold combinations convey luxury and quality
– Clean whites and silvers suggest purity and medical efficacy
– Earth tones and natural colors appeal to organic and craft market segments
– Muted color palettes comply with regulations while maintaining sophistication
Typography and Information Hierarchy:
– Clear, legible fonts ensure regulatory compliance and consumer understanding
– Hierarchical information organization prioritizes critical safety and dosing information
– Consistent typography systems across product lines build brand recognition
– Multilingual considerations for diverse market demographics

Luxury Positioning through sophisticated design elements:
– Minimalist aesthetics emphasizing quality over quantity
– Tactile surfaces providing premium feel and handling experience
– Metallic accents suggesting precision and craftsmanship
– Geometric patterns creating visual interest while maintaining sophistication
Artisanal and Craft Positioning:
– Hand-crafted appearances suggesting small-batch production
– Natural textures connecting to organic cultivation practices
– Vintage-inspired design elements appealing to traditional cannabis culture
– Personalized touches creating emotional connection with consumers
Pharmaceutical Aesthetics for medical cannabis products:
– Clinical color schemes building trust and professionalism
– Clear dosing information prominently displayed
– Medical symbols and certification indicators
– Accessibility features for patients with physical limitations
Patient-Centered Design:
– Easy-open mechanisms for patients with arthritis or limited dexterity
– Large, clear labeling for vision-impaired users
– Medication reminder features supporting treatment compliance
– Discrete packaging respecting patient privacy concerns
Lifestyle Integration for recreational consumers:
– Sleek, modern aesthetics fitting contemporary lifestyles
– Portable design for on-the-go consumption
– Social sharing features encouraging group consumption
– Customizable elements allowing personal expression
Experience-Focused Design:
– Ritual enhancement packaging that improves consumption experience
– Educational components building product knowledge
– Interactive elements engaging consumers beyond purchase
– Collectible aspects encouraging brand loyalty
Conclusion
The foundational elements explored in Part I—product diversity, regulatory complexity, and packaging innovation—establish the critical framework necessary for understanding the cannabis concentrate industry’s remarkable market dynamics. As we’ve seen, the intricate interplay between extraction technologies, compliance requirements, and consumer-facing design creates both significant barriers to entry and substantial opportunities for differentiation within this rapidly evolving sector. The sophisticated production methods required for premium concentrates like live rosin and sauce, combined with the navigational challenges of multi-state regulatory compliance and the strategic importance of packaging as both a safety mechanism and brand differentiator, directly influence market positioning, pricing strategies, and competitive advantages. Part II will build upon this foundation to examine the market forces driving this industry’s explosive growth, analyzing market size projections, competitive landscape dynamics, consumer behavior trends, and the investment opportunities emerging from the intersection of technological innovation and regulatory maturation that defines today’s cannabis concentrate marketplace.




